
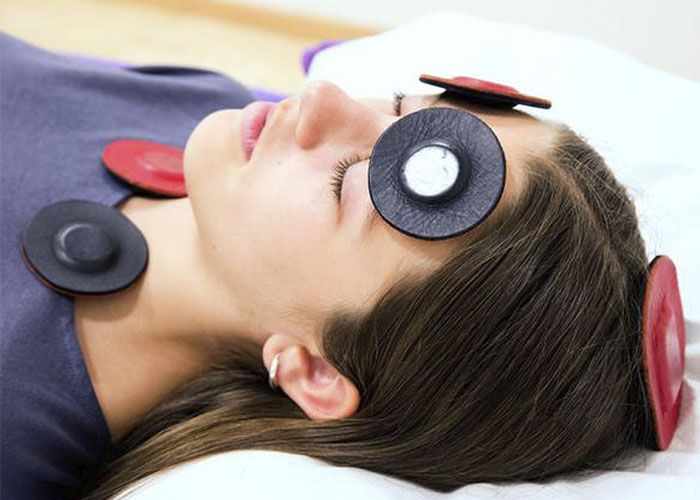
For practitioners working in complementary and integrative health fields, assessment is a critical foundation of effective practice. Within the context of applied biomagnetic therapy uk, assessment techniques are designed to identify energetic imbalances that may influence the body’s overall state of balance. Rather than focusing solely on symptoms, biomagnetic assessment seeks to understand patterns within the body’s bioenergetic system, allowing practitioners to tailor sessions with precision and intention.
Biomagnetic assessment techniques are rooted in observation, structured testing, and practitioner awareness. These methods aim to identify subtle energetic shifts that may not be visible through conventional diagnostic tools. For practitioners, developing skill in assessment is essential for delivering consistent, responsible, and client-centered biomagnetic sessions.
The Purpose of Assessment in Biomagnetic Practice
Assessment in biomagnetic practice serves a different role than diagnosis in conventional medicine. Practitioners do not diagnose medical conditions; instead, they assess energetic patterns, functional imbalances, and areas where the body may benefit from support. This distinction is fundamental to ethical and professional practice.
A well-conducted assessment helps practitioners determine appropriate magnet placement, session focus, and overall strategy. It also provides a structured way to monitor changes over time, supporting continuity and clarity in ongoing care. For practitioners, assessment is both a technical skill and an interpretive process that develops with experience.
Core Principles Behind Biomagnetic Assessment Techniques
Biomagnetic assessment is based on the idea that the body functions as an interconnected energetic system. Changes in one area may influence others, and imbalances often present as patterns rather than isolated points. Practitioners are trained to observe these patterns through structured techniques rather than assumptions.
Assessment techniques typically rely on consistency, repeatability, and practitioner neutrality. Maintaining an objective mindset allows practitioners to respond to what they observe rather than what they expect to find. This disciplined approach supports professional integrity and enhances client trust.
Biomagnetic Assessment in a Complementary Healthcare Context
Within integrative wellness environments, medical biomagnetic therapy in uk is often positioned as a supportive modality that complements conventional healthcare rather than replacing it. Practitioners working in this context must be especially mindful of scope, communication, and professional boundaries.
Assessment techniques are therefore framed around energetic balance and functional support. Practitioners may collaborate with other wellness professionals or encourage clients to maintain ongoing communication with their healthcare providers. This collaborative model reinforces the role of biomagnetic therapy as part of a broader wellness ecosystem.
Initial Client Consultation and Information Gathering
Before any physical assessment begins, practitioners typically conduct a thorough consultation. This stage allows practitioners to understand the client’s general wellbeing, lifestyle factors, and goals for the session. While no medical diagnosis is made, this information provides valuable context for energetic assessment.
Practitioners often look for patterns related to stress, sleep, physical activity, and overall vitality. These insights help guide assessment techniques and support a more individualized approach. Effective consultation also establishes rapport, which is essential for client comfort and cooperation during assessment.
Muscle Response and Feedback-Based Assessment Methods
One commonly discussed assessment approach in biomagnetic practice involves muscle response or feedback-based techniques. These methods rely on observing subtle changes in muscle tone or responsiveness as the body reacts to specific stimuli or positions.
For practitioners, precision and consistency are critical when using these techniques. Proper training helps ensure that assessments are performed ethically and reliably. Over time, practitioners learn to differentiate between meaningful responses and external influences such as tension or expectation.
Structural and Positional Observation Techniques
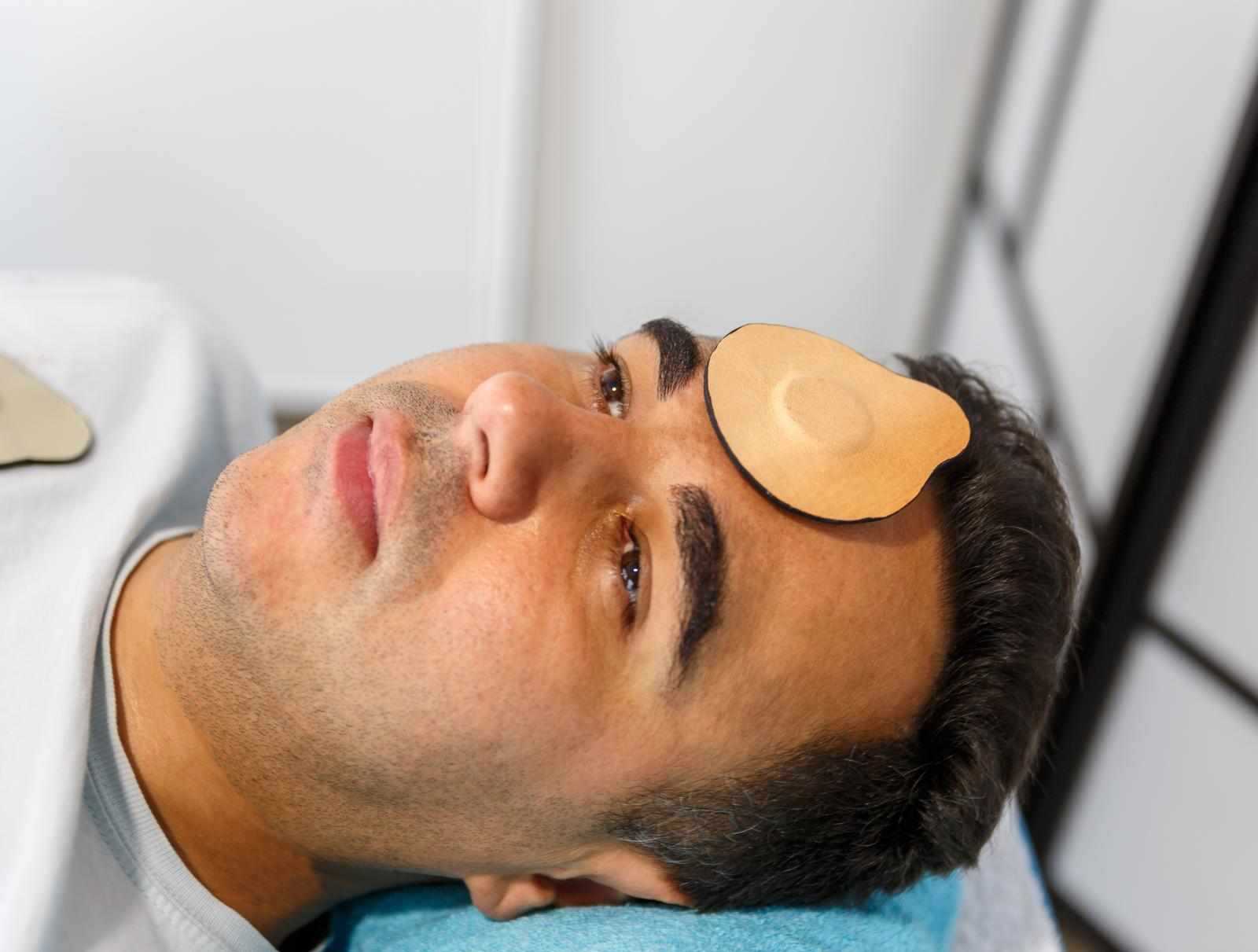
In addition to response-based methods, practitioners may observe structural or positional indicators during assessment. This can include noticing posture, alignment, or subtle asymmetries that may suggest energetic imbalance.
These observations are not diagnostic but serve as reference points within the biomagnetic framework. Practitioners often integrate this information with other assessment findings to form a coherent session plan. Developing observational skills enhances practitioner confidence and session effectiveness.
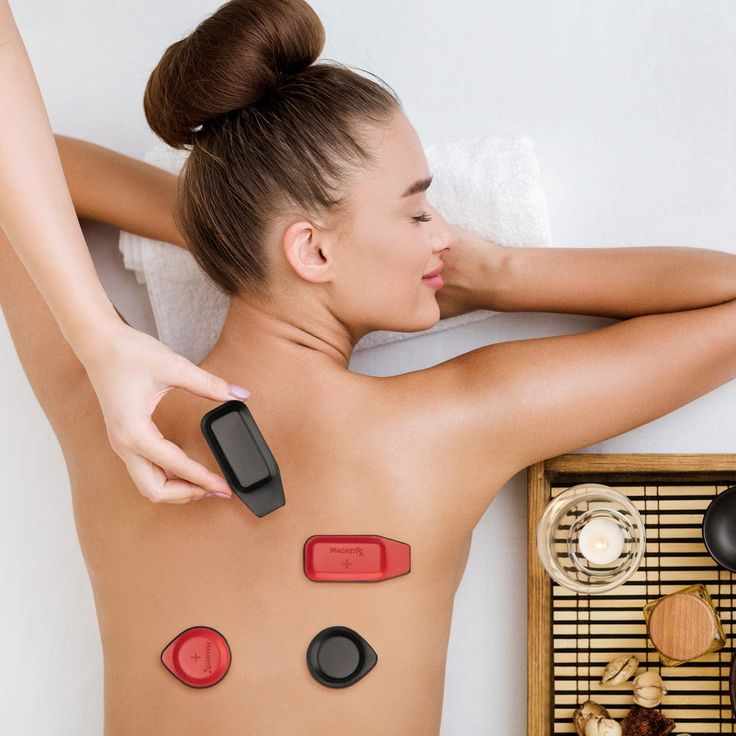
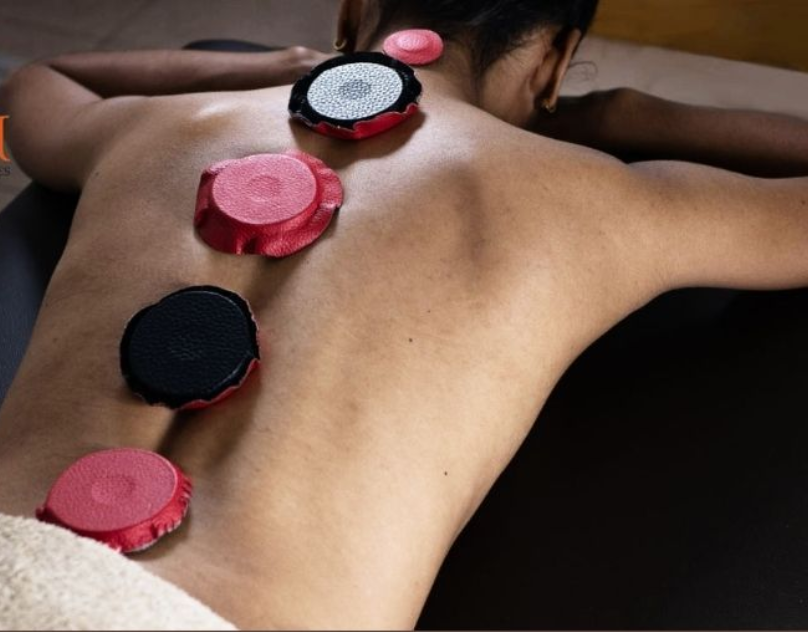
Mapping Energetic Patterns for Targeted Sessions
Assessment techniques are often used to create an energetic map that guides magnet placement. This mapping process helps practitioners determine which areas of the body may benefit from support during a session.
Rather than applying magnets randomly, practitioners rely on assessment findings to make informed decisions. This targeted approach supports consistency across sessions and allows practitioners to track changes over time. For clients, this structured method reinforces confidence in the practitioner’s professionalism.
The Role of Practitioner Awareness and Neutrality
A key element of effective biomagnetic assessment is practitioner awareness. Maintaining a neutral mindset reduces the risk of bias and ensures that assessments reflect genuine energetic responses rather than practitioner expectations.
Experienced practitioners often emphasize the importance of self-regulation, grounding, and presence during assessment. These qualities support clearer observation and enhance the practitioner-client dynamic. Over time, awareness becomes as important as technical skill in delivering reliable assessments.
Documentation and Session Tracking for Practitioners
Professional biomagnetic practice includes clear documentation of assessment findings and session outcomes. Recording observations allows practitioners to monitor progress, adjust approaches, and maintain continuity in care.
Documentation also supports ethical practice by providing transparency and accountability. For practitioners working in multidisciplinary settings, clear records help facilitate communication with other wellness professionals when appropriate.
Adapting Assessment Techniques for Individual Clients
No two clients present the same energetic patterns, which is why flexibility in assessment is essential. Practitioners learn to adapt techniques based on individual responsiveness, comfort, and session goals.
This adaptability is especially important when working with clients who are new to biomagnetic therapy. Clear explanation and gentle pacing help ensure that assessment techniques are both effective and respectful of client boundaries.
Ethical Considerations in Biomagnetic Assessment
Ethical practice is central to practitioner-focused assessment. This includes clear communication about the purpose of assessment, realistic expectations, and the complementary nature of biomagnetic therapy.
Practitioners must avoid making medical claims or interpretations beyond their scope. By maintaining ethical boundaries, practitioners protect both clients and the integrity of biomagnetic practice as a whole.
Ongoing Learning and Skill Development
Assessment techniques in biomagnetic practice evolve with experience and continued education. Practitioners often refine their skills through training, peer discussion, and reflective practice.
Ongoing learning supports consistency and helps practitioners stay aligned with best practices. This commitment to development is especially important in complementary health fields, where practitioner competence directly influences client experience.
Integrating Assessment Into a Professional Practice Model
For practitioners, assessment is not a standalone activity but part of a broader professional framework. It informs session planning, client communication, and long-term strategy. When integrated thoughtfully, assessment enhances both effectiveness and credibility.
A practitioner-focused approach emphasizes clarity, consistency, and responsibility. These qualities help position biomagnetic therapy as a respected complementary practice within the wider wellness landscape.
Concluding Reflections on Practitioner-Focused Assessment
A practitioner-focused look at biomagnetic assessment techniques highlights the importance of skill, awareness, and ethical responsibility. Assessment is the foundation upon which effective sessions are built, guiding magnet placement and supporting individualized care.
By approaching assessment with professionalism and neutrality, practitioners can offer structured, supportive sessions that align with the principles of complementary wellness. As interest in biomagnetic therapy continues to grow, high-quality assessment practices will remain central to its credibility and long-term development.
Conclusion
Biomagnetic assessment techniques form the backbone of responsible and effective biomagnetic practice. For practitioners, these methods provide a structured way to observe energetic patterns, guide magnet placement, and support individualized sessions without crossing into medical diagnosis. When applied with neutrality, professional training, and ethical awareness, assessment becomes a powerful tool for consistency and clarity in practice. As interest in biomagnetic therapy continues to expand, strong assessment skills help practitioners maintain credibility and client trust. Ultimately, a thoughtful, well-documented assessment process supports balanced outcomes and reinforces biomagnetic therapy’s role as a complementary, non-invasive approach to holistic wellbeing.








Write a comment ...